Chapter 7 - Storing Organizational Information - Database
RELATIONAL DATABASE FUNDAMENTALS
- Information is everywhere in an organization
- Information is stored in databases
ü Database – maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people (employees), and places (warehouses)
- Database models include;
ü Hierarchical database model – information is organized into a tree-like structure (using parent/child relationships) in such a way that it cannot have too many relationships.

ü Network database model – a flexible way of representing objects and their relationships

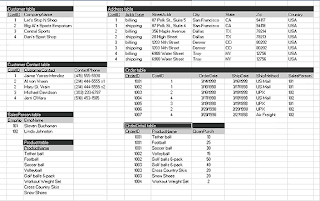
ü Relational database model – stores information in the form of logically related two-dimensional tables

ENTITIES AND ATTRIBUTES
- Entity – a person, place, thing, transaction, or event about which information is stored
ü The rows in each table contains the entities
- Attributes (fields, columns) – characteristics or properties of an entity class
ü The columns in each table contain the attributes
KEYS AND RELATIONSHIPS
- Primary keys and foreign keys identity the various entity classes (tables) in the database
ü Primary key – a fields (or group of fields) that uniquely identities a given entity in a table
ü Foreign key – a primary key of one table that appears an attribute in another table and acts to provide a logical relationships among the two tables
RELATIONAL DATABASE ADVANTAGES
- Database advantages from a business perspective include;
ü Increased flexibility
ü Increased scalability and performance
ü Reduced information redundancy
ü Increased information integrity (quality)
ü Increased information security
INCREASED FLEXIBILITY
- A well-designed database should;
ü Handle changes quickly and easily
ü Provide users with different views
ü Have only one physical views² Physical view – deals with the physical storage of information on a storage device
ü Have multiple logical views² Logical view – focuses on how users logically access information
INCREASED SCALABILITY AND PERFORMANCE
- A database must scale to meet increased demand, while maintaining acceptable performance levels
ü Scalability – refers to how well a system can adapt to increased demands
ü Performance – measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction
REDUCED INFORMATION REDUNDANCY
- Databases reduce information redundancy
ü Redundancy – the duplication of information or storing the same information in multiple places
- Inconsistency is one of the primary problems with redundant information
INCREASED INFORMATION SECURITY
- Information is an organization asset and must be protected
- Databases offer several security features including;
ü Password – provides authentication of the user
ü Access level – determines who has access to the different types of information
ü Access control – determines types of user access, such as read-only access
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
- Database management systems (DBMS) – software through which users and application programs interact with a database

DATA-DRIVEN WEB SITES
- Data-driven Web sites – an interactive Web site kept constantly updated and relevant to the needs of its customers through the use of database

DATA-DRIVEN WEB SITE BUSINESS ADVANTAGES
- Development
- Content Management
- Future Expandability
- Minimizing Human Error
- Cutting Production and Update Costs
- More Efficient
- Improved Stability
DATA-DRIVEN BUSINESS INTELLIGENT
- BI in a data-driven Web site

INTEGRATING INFORMATION AMONG MULTIPLE DATABASES
- Integration – allows separate systems to communicate directly with each other
ü Forward integration – takes information entered into a given system and sends it
automatically to all downstream systems and processes
automatically to all downstream systems and processes

ü Backward integration – takes information entered into a given system and sends it
automatically to all upstream systems and processes
automatically to all upstream systems and processes

- Building a central repository specifically for integrated information

No comments:
Post a Comment